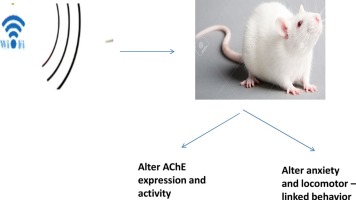
Effects of Telecommunication Mast Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) on Exposed Rats (Rattus norvegicus)
Downloads
Background: The safety of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) from modern telecommunication devices is controversial as some studies reported negative effects, while others reported no effects. Thus, more studies are necessary to clear the controversy, so as to design appropriate precautionary and palliative measures if found toxic.
Objective: This study was conducted to determine the effects of telecommunication mast EMR on selected health indices of rats (Rattus norvegicus).
Materials and Methods: Twenty-four (24) rats were divided into two groups of 12 rats each. Group 1 was made the control, while group 2 was exposed to 18000 MHz EMR at 50 m from a telecommunication mast. The weight, body temperature, reproductive activities, and reactions of the rats were observed for 60 days. Thereafter, the rats were sacrificed and their blood parameters, liver function, and histology were examined.
Results: The exposed rats were less active, weighed and reproduced less, had lower offspring survival rates and insignificantly (P > 0.05) elevated body temperature. The white blood cells (WBC) of the exposed rats were significantly increased (P < 0.05), while the packed cell volume (PCV), hemoglobin (Hb), red blood cells (RBC), and lymphocytes were reduced. The aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and total protein (TP) of the exposed rats were significantly increased, while the albumin (ALB) was significantly reduced. The ovary, lung, and kidney tissues of the exposed rats showed no abnormalities, but necrosis of the hepatocytes and fat were observed in their livers and the skins, respectively.
Conclusion and Recommendation: It is concluded that electromagnetic radiation (EMR) from modern telecommunication devices harmed the health of exposed rats. It is inferred from the results that EMR has negative effects on the health of mammals. Hence, it is advisable not to site telecommunication masts close to dwelling places.
Copyright (c) 2020 Tajudeen Yahaya, Esther Oladele, Obaroh Israel, Jamilu Bala, Abdulhakeem Haruna, Abubakar Muhammad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
- I am authorized by my co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- I warrant, on behalf of myself and my co-authors, that:
- the article is original, has not been formally published in any other peer-reviewed journal, is not under consideration by any other journal and does not infringe any existing copyright or any other third party rights;
- I am/we are the sole author(s) of the article and have full authority to enter into this agreement and in granting rights to Springer are not in breach of any other obligation;
- the article contains nothing that is unlawful, libellous, or which would, if published, constitute a breach of contract or of confidence or of commitment given to secrecy;
- I/we have taken due care to ensure the integrity of the article. To my/our - and currently accepted scientific - knowledge all statements contained in it purporting to be facts are true and any formula or instruction contained in the article will not, if followed accurately, cause any injury, illness or damage to the user.
- I, and all co-authors, agree that the article, if editorially accepted for publication, shall be licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0. If the law requires that the article be published in the public domain, I/we will notify Springer at the time of submission, and in such cases the article shall be released under the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver. For the avoidance of doubt it is stated that sections 1 and 2 of this license agreement shall apply and prevail regardless of whether the article is published under Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 or the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver.
- I, and all co-authors, agree that, if the article is editorially accepted for publication in Haramaya Journals, data included in the article shall be made available under the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver, unless otherwise stated. For the avoidance of doubt it is stated that sections 1, 2, and 3 of this license agreement shall apply and prevail.